Which Vitamin Is Part of the Structure of Acetyl Coa
The coenzyme is involved in transfer of acyl-groups. The sulfhydryl group is where many different molecular groups attach including acetyl CH 3 -CO- and acyl groups RCO-.

Acetyl Coa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
CoA is an important one which plays a vital role in many biochemical reactions of metabolism.

. Coenzyme A has a complex structure consisting of an adenosine triphosphate a pantothenic acid which is a B-vitamin and cysteamine. Structure of Acetyl CoA The head nucleotide the body vitamin B5 and the tail beta-merceptoehtylamine make up the whole beast. ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae whereas it is a large multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm of most.
Acetyl-CoA acetyl coenzyme A is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Acetyl-CoA represents a key node in metabolism due to its intersection with many metabolic pathways and transformations. What happens when acetyl CoA is abundant.
An acetyl group is. Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Furthermore they play an important role in the energy production of the body through catabolism.
Coenzyme A CoASH or CoA consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid through an amide linkage and 3-phosphorylated ADP. Glycerol to Acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA can be synthesized from pyruvate.
Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid through an amide linkage and 3-phosphorylated ADP. The R group can be variable. This reaction is catalyzed by phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase.
Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle Krebs cycle. The acetyl group indicated in blue in the structural diagram on the right of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. A cysteine molecule is added to the 4-phosphopantothenate and the new molecule formed is 4- phospho- N-pantothenoylcysteine.
Pyridoxal phosphate catalyses transamination decarboxylation condensation deamination and trans-sulphuration. Acetyl CoA and acyl CoA are two types of coenzymes important in fatty acid metabolism. It also acts as a biological acetylating agent.
The sulfhydryl -SH group of cysteamine moiety of this coenzyme forms a thioester with the carboxyl -COOH group of the acyl-compound such as acetic acid. Coenzyme A CoASH or CoA consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid through an amide linkage 2 and 3-phosphorylated ADP. Triglycerides are broken down into simpler pieces and is seperated.
Both of these have a similar structure and their structural components include carbonyl group R group and a coenzyme A group. Coli Metabolome Database ECMDB. Biological functions of Vitamin B6 Pyridoxal phosphate.
Its structure is synthesized in a step by step process. We offer the following conceptual model for. CoA consists of a nucleotide head adenine ribose phosphate a vitamin B5 body and a beta-mercaptoethylamine tail which contains a sulfhydryl group.
Glycerol and fatty acids will follow different paths of being converted. Emerging evidence reveals that cells monitor the levels of acetyl-CoA as a key indicator of their metabolic state through distinctive protein acetylation modifications dependent on this metabolite. Medical Subject Headings MeSH Acetyl-CoA is a metabolite found in Escherichia coli strain K12 MG1655.
Now well talk about the acetyl part. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities biotin carboxylase and carboxyltransferase. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.
Acetyl CoA participates in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and sterols in the oxidation of fatty acids and in the metabolism of many amino acids. When ATP supplies are abundant the acetyl-CoA can be diverted to other purposes like energy storage in the form of fatty acids. Acetyl CoA is used for synthesis of ketone bodies acetone -hydroxy butyrate and acetoacetate V.
Niacin or Vitamin B3 seeing as though it catalyzes redox reactions related to energy metabolism which would ultimately lead to the citric acid cycle or. Converting of Acetyl CoA Step 3. When ATP is needed this acetyl-CoA can enter the Krebs cycle to drive oxidative phosphorylation.
Which vitamin is part of the structure of coenzyme A ie of acetyl CoA thiamin from NUTR 251 at Pennsylvania State University World Campus.

Biotin Fatty Liver Detox Fatty Liver Acetyl Coa

Schematic Representation Of The Key Role Of Acetyl Coa In The Central Download Scientific Diagram

Acetyl Coa The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
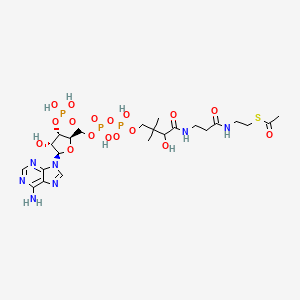
Acetyl Coa C23h38n7o17p3s Pubchem

Acetyl Coa The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Acetyl Coa The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

No comments for "Which Vitamin Is Part of the Structure of Acetyl Coa"
Post a Comment